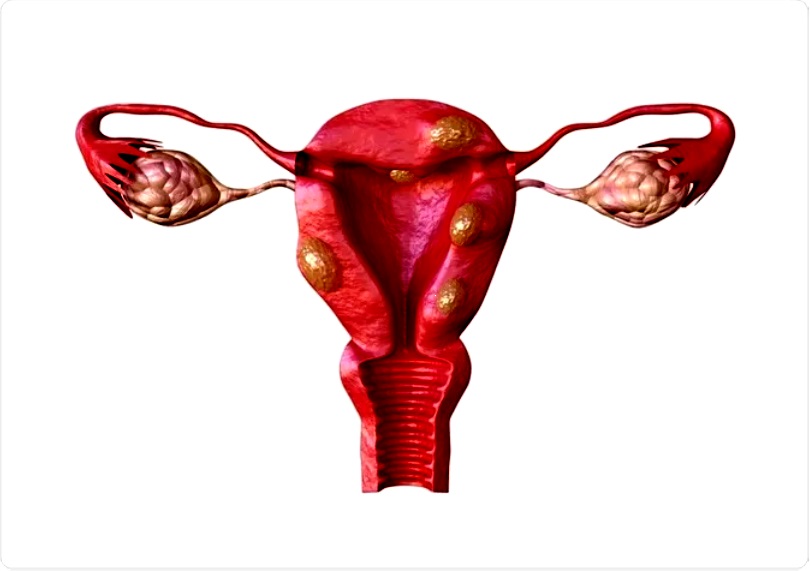
Uterine fibroids are a common problem for women. Uterine fibroids, also known as myomas, leiomyomas, or fibromyomas, are benign tumors that grow in the uterus. They are non-cancerous growths that form in the uterus. Fibroids can range in size from very small to very large. Most women with uterine fibroids don’t have any symptoms. However, some women may have pain, heavy periods, or problems getting pregnant. They are the most common tumors found in women and can occur at any age, but are most common in women aged 30 to 50.
They are very common, occurring in about one-third of women by the time they reach menopause. While their cause is unknown, there are a number of factors that may increase a woman’s risk of developing uterine fibroids, including age, race, and family history.
What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are a common and benign tumor found in women. While the cause is unknown, it is thought to develop from the smooth muscle cells in the uterus. Symptoms can include pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, problems with urination or bowel movements, constipation and an enlarged uterus. Fibroids can also affect fertility and increase the risk for miscarriage or preterm birth. If you experience any of these symptoms, see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Pelvic pain

Many women experience pelvic pain as a symptom of uterine fibroids. While the pain can vary from woman to woman, it is typically described as a dull, constant ache in the lower abdomen and pelvis. Some women also experience cramping, pressure, and heaviness in the area. The pain can be accompanied by other symptoms of uterine fibroids such as irregular periods, bleeding between periods, and difficulty emptying the bladder or having a bowel movement. If you are experiencing pelvic pain, see your doctor to determine the cause and get treatment.
Heavy mensural bleeding
For most women, uterine fibroids don’t cause any problems. However, for some women, uterine fibroids can cause heavy mensural bleeding. If you experience heavy mensural bleeding, it’s important to see your doctor to find out if you have uterine fibroids. In fact, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, up to 50% of women who have uterine fibroids report experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. If you are experiencing heavy mensural bleeding, there are some things you can do to manage your symptoms.
One thing you can do is track how much blood you are losing during your period. This will help you to better understand how heavy your bleeding is and whether or not it is impacting your daily life. You can also keep a record of other symptoms you are experiencing, such as pain or pelvic pressure. This information can be helpful for your doctor in diagnosing and treating your uterine fibroids.
Problems with urination or bowel movements
Many women experience problems with urination or bowel movements when they have uterine fibroids. Urinary problems may include difficulty emptying the bladder, a feeling of fullness in the bladder, and urinary tract infections. Bowel problems may include constipation and difficulty passing stool.
These symptoms can be caused by the size and location of the fibroids. Fibroids that grow near the uterus or bladder can put pressure on these organs, which can lead to urinary or bowel problems. Fibroids that grow on the outside of the uterus can press against other organs in the pelvis, such as the bladder and intestines. This pressure can also cause urinary or bowel problems. If you are experiencing any urinary or bowel problems, see your doctor.
Constipation
One common symptom of uterine fibroids is constipation. This is because the enlarged uterus can put pressure on the rectum and intestines, which can slow down or stop the flow of stool. This can be caused by a variety of things, including the build-up of scar tissue in the uterus. Constipation can also cause severe abdominal pain and bloating. If you’re constipated, you may notice that you’re having difficulty passing stools or that your stools are hard and dry. This can lead to pain and discomfort, as well as other issues like hemorrhoids.
An enlarged uterus
The uterus may be enlarged because the fibroid is pushing it out of shape or because it is filling up with fluid. An enlarged uterus can also cause back pain, pelvic pain, and difficulty walking or moving. If you have an enlarged uterus, it’s important to talk to your doctor to find out if you have uterine fibroid. If left untreated, an enlarged uterus can lead to infertility.
How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?

If you’re experiencing any of the above symptoms, see your doctor. They’ll likely ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. Depending on your symptoms, they may also order imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI or hysteroscopy to help diagnose the fibroids.
Physical exam
Uterine fibroids are often found during a routine physical exam. During the physical exam, the doctor will feel for any masses or abnormalities in the uterus or ask about your menstrual history. If uterine fibroids are suspected, additional tests may be ordered such as an ultrasound to confirm their presence and size.
Ultrasound
Uterine fibroids are diagnosed with a pelvic ultrasound. During the ultrasound, the doctor will measure the size and shape of the uterus and look for any evidence of uterine fibroids. If uterine fibroids are found, additional tests may be needed to determine if they are causing the woman’s symptoms.
What treatments are available for uterine fibroids?
There are a few different treatments available for uterine fibroids, depending on the severity of the condition and the woman’s wishes. Some treatments include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
Medication
Medication can include over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or aspirin to help relieve pain and inflammation. Prescription medications may useful to shrink the tumors or to reduce heavy bleeding. The medications are: hormonal therapy, pain relief medications, and blood thinners.
Hormonal therapy: There are a number of medications to help shrink the fibroids and relieve the symptoms. These medications include hormonal therapies like birth control pills and GnRH agonists, as well as medications that suppress estrogen production like aromatase inhibitors. Some common hormonal therapies used to treat uterine fibroids include birth control pills and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists.
Pain relief medications: If you’re experiencing pain due to uterine fibroids, your doctor may prescribe pain relief medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
Blood thinner: Blood thinners help to reduce the size of the fibroids and can improve symptoms such as heavy periods.
Surgery
Surgery is useful to remove the fibroid tumors or to correct other problems caused by the tumors, such as blockages in the intestines or urinary tract. If medication fails to provide relief, surgery is the next recommendation. There are a number of different surgical procedures to treat uterine fibroids. There are a few different types of surgery to treat uterine fibroids. One type of surgery is myomectomy.
Are there any risks associated with uterine fibroid treatments?
There are many potential risks associated with uterine fibroid treatments. Some of the more common risks include: infection, bleeding, and scarring. In some cases, uterine fibroid treatments may also cause infertility or problems with future pregnancies. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of each treatment option with your doctor before making a decision.
Infection: There are many risks associated with uterine fibroid treatments, the most common of which is infection. Anytime you go through surgery there is always a risk of infection. In the case of uterine fibroid treatments, this can be a particularly serious complication. Women are particularly susceptible to infection after surgery and if it is untreated quickly and aggressively, it can lead to serious health problems.
In order to reduce the risk of infection, doctors will often prescribe antibiotics both before and after surgery. Another potential risk is damage to surrounding organs, such as the bladder or bowel. However, this is a rare occurrence and can usually avoidable if surgeons are careful during surgery. Finally, there is always a small risk that the fibroid may not be completely removed, resulting in a recurrence of symptoms.
Bleeding: Bleeding can occur either during or after surgery. In some cases, this bleeding may be severe enough to require a blood transfusion. This can be caused by the procedure itself or by the fibroids themselves.
Scarring: One risk that is often associated with these treatments is scarring. Scarring can occur when the surgeon cuts or burns the tissue to remove the fibroids. It can also occur when the staples or stitches used to close the surgical wound become infected. If too much scarring develops, it can cause problems with future pregnancies, such as difficulty conceiving or miscarriage. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove scar tissue.
Final words
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop from the muscle layer of the uterus. While they are not cancerous, they can cause problems such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility. Some women may choose to have surgery to remove the fibroids, while others may prefer to manage them with medication or watch and wait. New research suggests that there may be a link between uterine fibroids and breast cancer. However, more research is needed to determine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the two conditions.